
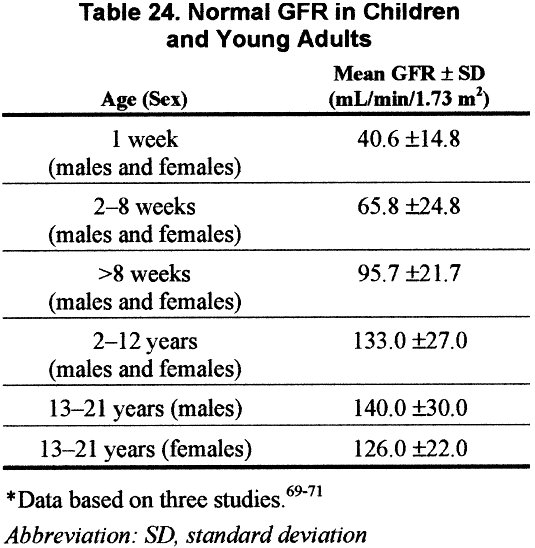
The earlier that the signs and symptoms of chronic kidney disease in diabetes are detected, the better, as it will reduce the chance of progression to advanced kidney disease and the need for dialysis or transplant.Progression of chronic kidney disease in diabetes can also be slowed through the use of medications that disrupt the renin angiotensin aldosterone system. The development and progression of renal damage in diabetes can be reduced and slowed through intensive glycemic control and optimization of blood pressure.All individuals with chronic kidney disease should be considered at high risk for cardiovascular events and should be treated to reduce these risks.Identification of chronic kidney disease in people with diabetes requires screening for proteinuria, as well as an assessment of serum creatinine converted into an estimated glomerular function rate (eGFR).Threatening diseases like stroke and heart attack. If you have high blood pressure you are at risk of developing life Stage 2 hypertension is considered 140/90 mm Hg. The American Academy of Cardiology defines high blood pressure slightlyĭifferently. If either one of those numbers is higher, you have high The guidelines now state that blood normal blood The American College of Cardiology released new guidelines for Systolic and diastolic are the two readings in which blood pressure is People do not know that they have high blood pressure because it often has no Hypertension (1 in 3 adults), and only half of them are able to manage it. High blood pressure (hypertension) is a disease in which pressure within theĪrteries of the body is elevated. The BUN-to-creatinine ratio generally provides more precise information about kidney function and its possible underlying cause compared with creatinine level alone.
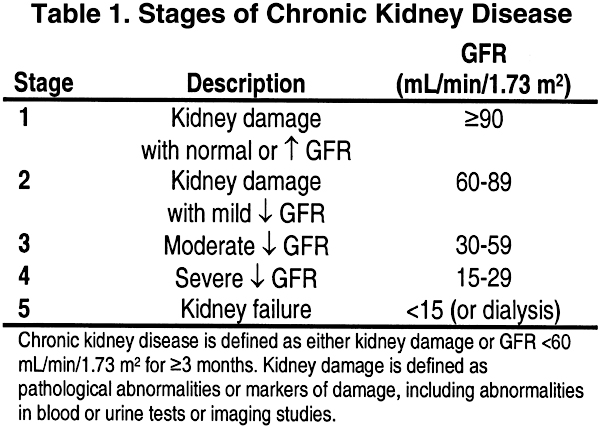

Urea is also a metabolic byproduct that can build up if kidney function is impaired. in males (normal levels may vary slightly between labs).īlood urea nitrogen (BUN) level is another indicator of kidney function. Normal creatinine clearance for healthy women is 88-128 mL/min. The creatinine levels in both urine and blood are determined and compared. Creatinine clearance can also be more directly measured by collecting a 24-hour urine sample and then drawing a blood sample.The formula is 140 minus the patient's age in years times their weight in kilograms (times 0.85 for women), divided by 72 times the serum creatinine level in mg/dL. It can be calculated (estimated) by a formula using serum (blood) creatinine level, patient's weight, and age.The creatinine clearance can be measured in two ways. This is referred to as creatinine clearance and it estimates the rate of filtration by kidneys (glomerular filtration rate, or GFR). It is for this reason that standard blood tests routinely check the amount of creatinine in the blood.Ī more precise measure of kidney function can be estimated by calculating how much creatinine is cleared from the body by the kidneys. Abnormally high levels of creatinine thus warn of possible malfunction or failure of the kidneys. Elevated creatinine level signifies impaired kidney function or kidney disease.Īs the kidneys become impaired for any reason, the creatinine level in the blood will rise due to poor clearance of creatinine by the kidneys. Creatinine is a fairly reliable indicator of kidney function. The kidneys maintain the blood creatinine in a normal range.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
